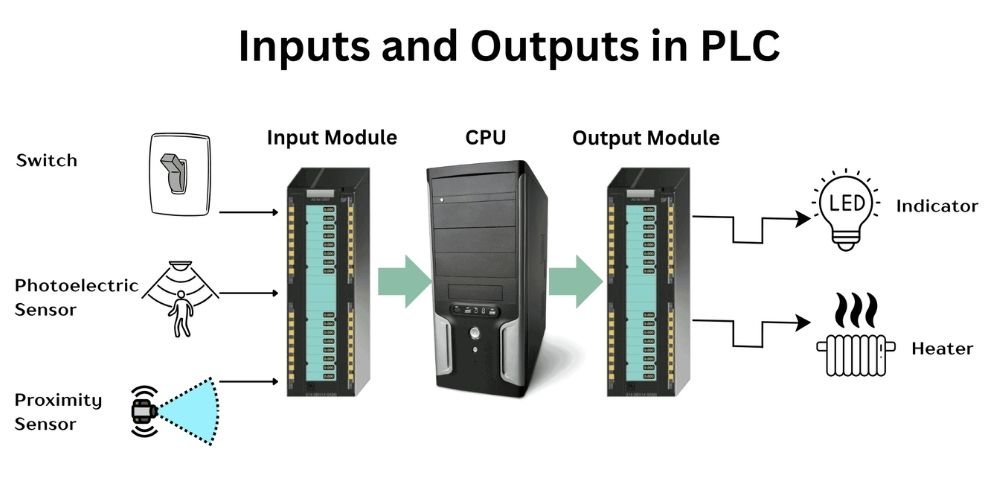
Understanding PLC Input and Output: The Foundation of Automation
In the world of industrial automation, nothing happens without PLC input and output. These are the essential channels that allow a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) to interact with real-world machines and processes. Whether you're an automation beginner or a technician refining your skills, understanding how PLC input and output works—and knowing the types involved—is a critical step in mastering control systems. Inputs are the signals a PLC receives from the outside world. These can come from: Outputs are the actions the PLC controls in the real world. These could activate: Think of inputs as "what’s happening" and outputs as "what to do about it." How PLC Input and Output Work Together The PLC input and output system forms a loop: Here’s a basic PLC input output list to help you visualize common I/O devices used in automation: These inputs and outputs are wired to the PLC’s I/O modules, and the type of signal—digital or analog—determines how the PLC processes them. Understanding this difference is crucial for choosing the right module and designing effective logic. Modern PLCs are modular, meaning you can mix and match input and output modules based on your needs: Each module is connected to your PLC’s CPU and is programmed via PLC software such as RSLogix, TIA Portal, or GX Works. Let’s look at a practical setup: The PLC input and output list for this system will be clearly labeled in the control panel, making troubleshooting and expansion easier. The PLC input and output system is the core of any automated process. Whether you’re building a simple machine or a complex production line, knowing how to select, wire, and program I/O devices ensures reliable performance. And with a solid PLC input output list, you can easily manage installations, troubleshoot issues, and scale up with confidence. Mastering I/O basics gives you the foundation to move forward in automation—toward motion control, PID loops, and IoT integration. Inputs bring real-world signals to the PLC; outputs let the PLC control external devices. Push buttons, limit switches, proximity sensors, and temperature sensors. Yes, most PLCs support both, but you need the appropriate I/O modules. Usually 24V DC for industrial PLCs, but other options (like 120V AC) exist. List all sensors (inputs) and actuators (outputs) used in your system, along with signal types and PLC terminal numbers.What Are Inputs and Outputs in PLC?
This process happens in milliseconds—allowing real-time control and decision-making in industrial systems.PLC Input Output List: Common Devices
Type Device Example Signal Type Input Push Button Digital (On/Off) Input Limit Switch Digital Input Temperature Sensor (RTD) Analog (Variable) Input Proximity Sensor Digital Output Relay Digital Output Motor Starter Digital Output Analog Valve Actuator Analog (0-10V or 4-20mA) Output Alarm Buzzer or Indicator Digital Digital vs. Analog Inputs and Outputs
Digital Inputs/Outputs
Analog Inputs/Outputs
Types of PLC I/O Modules
Real-World Example: PLC Inputs and Outputs in a Conveyor System
Inputs
Outputs
Best Practices for PLC I/O Design
Conclusion: Why Understanding PLC Input and Output MattersFAQs: PLC Input and Output
Q1: What is the difference between input and output in PLC?
Q2: What are common examples of PLC inputs?
Q3: Can a PLC have both analog and digital inputs?
Q4: What is the typical voltage for PLC inputs?
Q5: How do I make a PLC input output list?
Related Blogs