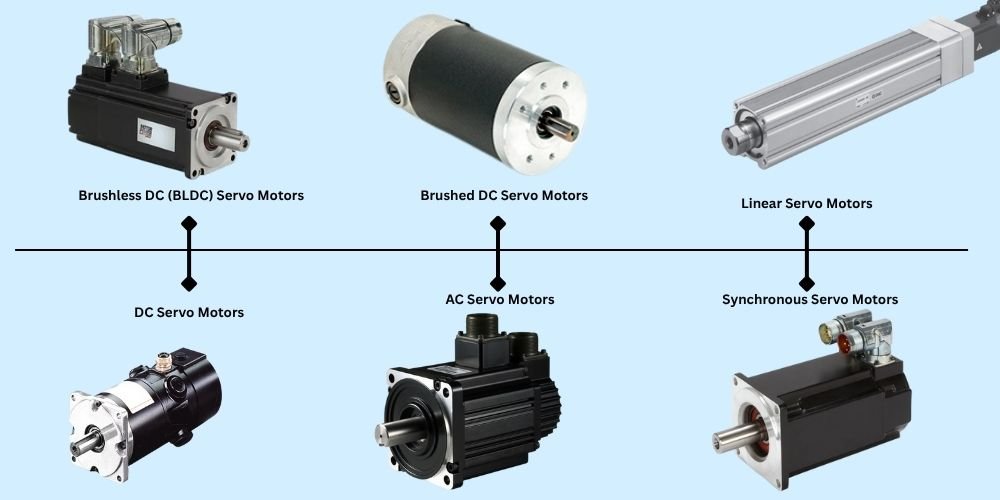
Types of Servo Motors Choosing the Right One for Your Application
Servo motors are key components in systems where precise control of motion is needed—like robotics, automation, CNC, and medical devices. But with various servo motor types available, it’s essential to understand their working styles, benefits, and limitations before selecting one. Below are the most common types of servo motors, along with deeper descriptions to help you decide what’s best for your application. Description: Best for: Description: Best for: Description: Best for: Description: Best for: Description: Best for: Description: Best for: Description: Best for: Each type of servo motor brings something unique: Selecting the right servo motor means balancing cost, control needs, size constraints, and load demands.1. AC Servo Motors
AC servo motors are powered by alternating current and are known for high torque, precision, and speed stability. They’re used where consistent performance is required under varying loads and environmental conditions. These motors typically come with built-in encoders for feedback and are widely supported by industrial servo drives.2. DC Servo Motors
DC servo motors use direct current and are generally easier to control. They have a faster response time due to lower inertia and are ideal for systems that need rapid start-stop cycles. However, they wear out quicker if brushed and are better suited for light-to-medium tasks.3. Brushless DC (BLDC) Servo Motors
These motors remove the mechanical brushes and commutators found in traditional DC motors. BLDC servos offer high efficiency, less noise, longer lifespan, and reduced maintenance. They work seamlessly in closed-loop systems and are perfect for compact applications needing continuous motion and reliability.4. Brushed DC Servo Motors
Brushed DC servo motors are simpler in design and more affordable. They are great for applications where cost matters more than long-term durability. However, brushes can wear out over time, requiring periodic maintenance. Still, they remain popular for basic motion control tasks.5. Linear Servo Motors
Linear servo motors provide straight-line motion directly, eliminating the need for rotary-to-linear converters like screws or belts. This increases efficiency and precision. They operate with zero backlash and are commonly used in advanced systems that demand micron-level accuracy.6. Synchronous Servo Motors
These motors run in sync with the input AC frequency, meaning their shaft rotates exactly with the supply signal. They are extremely stable under load and are ideal when the application needs constant speed and timing accuracy. Often used in precision cutting, feeding, and indexing tasks.7. Asynchronous Servo Motors
Also called induction-type servo motors, these are similar to standard induction motors but adapted for servo applications. They are less precise than synchronous types but offer robustness and cost efficiency, especially in general automation tasks where extreme precision isn’t critical.Final Thoughts